45 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › FluorescenceFluorescence - Wikipedia Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.It is a form of luminescence.In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. Fluorescent Microscopy - SERC A fluorescence microscope is much the same as a conventional light microscope with added features to enhance its capabilities. The conventional microscope uses visible light (400-700 nanometers) to illuminate and produce a magnified image of a sample. A fluorescence microscope, on the other hand, uses a much higher intensity light source which ...
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.

Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
Genetically encoded fluorescent tags - Molecular Biology of ... by K Thorn · 2017 · Cited by 98 — These tags have revolutionized cell biology by allowing nearly any protein to be imaged by light microscopy at submicrometer spatial ...GFP: green fluorescent proteinER: endoplasmic reticulumTMP: trimethoprimYFP: yellow fluorescent proteinTYPES OF FLUORESCENT... · INTRINSICALLY... · PHOTOCHROMIC TAGS Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Epifluorescence microscopes: The most common type of fluorescence microscope in which, excitation of the fluorophore and detection of the fluorescence are done through the same light path (i.e. through the objective).; Confocal microscope: In this type of fluorescence microscope, high‐resolution imaging of thick specimens (without physical sectioning) can be analyzed using fluorescent ... Light Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics 2.5.8.1 Fluorescent Labels. Light microscopy (LM) has undoubtedly become a widely used method in cell biology, and it is thus hard to overestimate its importance in the field. The abundance of currently available fluorescent probes, the advent of clonable fluorescent indicators, as well as the ubiquitous use of fluorescence LM (FM) has allowed ...
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. promocell.com › cell-culture-basics › fluorescentFluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Definition Fluorescent labeling is the process of binding fluorescent dyes to functional groups contained in biomolecules so that they can be visualized by fluorescence imaging (nature.com). The availability of new fluorophores has dramatically changed the possibilities for the sensitive detection of biomolecules and the analysis of their interactions. Improved fluorescent dyes are now ... Fluorescence Microscopy & Cell Imaging | Research | UNM Cancer Center Imaging. The Fluorescence Microscopy and Cell Imaging Shared Resource aids basic and physician researchers to image samples and publish high profile articles that: Elucidate cell and molecular mechanisms of cancer, immunologic, infectious, metabolic, neurologic and vascular diseases. Evaluate therapeutic efficacy in cells and patient samples. Light Sheet-based Fluorescence Microscopy of Living or Fixed and ... The observation of Tribolium embryos with light sheet-based fluorescence microscopy has multiple advantages over conventional widefield and confocal fluorescence microscopy. ... suggests five fluorescent dyes to label intracellular structures of fixed embryos and provides information on data post-processing for the timely evaluation of the ... A quick guide to light microscopy in cell biology - PMC Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes (fluorophores), which are molecules that absorb one wavelength of light (the excitation wavelength) and emit a second, longer wavelength of light (the emission wavelength). Most molecules in the cell are not very fluorescent, so fluorescent labels to be imaged are typically introduced by the ...
A chip-scale microscope for high-throughput fluorescence imaging Conventional light microscopy has been instrumental for studying cells and microorganisms; fluorescence microscopy enabled visualization of even smaller cell features by selectively adding ... pages.zeiss.com › rs › 896-XMS-794Principles of Fluorescence and Fluorescence Microscopy Fluorescence Microscopy Author: Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Germany Date: May 2019 Fluorescence is the property of atoms and molecules, so called fluorophores, to absorb light at a particular wavelength and to subsequently emit light of longer wavelength. Fluorescence microscopy can be based on autofluorescence or the addition of fluorescent dyes. In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images Microscopy is a central method in life sciences. Many popular methods, such as antibody labeling, are used to add physical fluorescent labels to specific cellular constituents. ... (ISL), reliably predicts some fluorescent labels from transmitted-light images of unlabeled fixed or live biological samples. ISL predicts a range of labels, such as ... A guide to super-resolution fluorescence microscopy In principle, CLSM can achieve a better resolution than wide-field fluorescence microscopy but, to obtain a significant practical advantage, the pinhole needs to be closed to an extent where most of the light is discarded (Heintzmann et al., 2003). Alternatively, an interferometric detection technique could be used (Wicker et al., 2009).
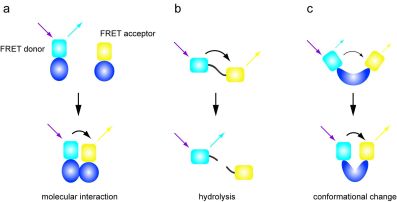
Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells. ... phenotypes can be detected via expressed fluorescent labels ... Fluorescence Microscopy - Explanation and Labelled Images A fluorescence microscope works by combining the magnifying properties of the light microscope with fluorescence emitting properties of compounds. Fluorescence microscopy uses a high-intensity light source that excites a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore in the sample observed. ... and by doing so, highlight (or "label") the nuclei ... Fluorescence Microscopy vs. Light Microscopy - Medical News This light is in the 400-700 nm range, whereas fluorescence microscopy uses light with much higher intensity. The usefulness of traditional light microscopy is hampered by the fact that it uses ... › applications › fretBasics of FRET Microscopy | Nikon’s MicroscopyU The first fluorescent protein biosensor was a calcium indicator named cameleon, constructed by sandwiching the protein calmodulin and the calcium calmodulin-binding domain of myosin light chain kinase (M13 domain) between enhanced blue and green fluorescent proteins (EBFP and EGFP). In the presence of increasing levels of intracellular calcium ...

Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy ...
› microscopy › intSmart Microscope for Lab Routine and Research - ZEISS In the past, documenting samples with multiple fluorescent labels in your routine lab could be time consuming. To get best image quality, you needed to manually switch filters, adjust illumination intensities and exposure times and to snap each single channel image. For four different channels, this could sum up to 15 steps and clicks.
Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics M. Heilemann, in Comprehensive Biophysics, 2012 Abstract. Fluorescence microscopy is a valuable toolbox to study cellular structures and dynamics spanning scales from the single molecule to the live animal. The spatial resolution that can be achieved with any light-based microscopy is however limited to about 200 nm in the imaging plane and >500 nm along the optical axis.
Fluorescence Microscopy - ChemBAM The technique of fluorescence microscopy has become an essential tool in biology and the biomedical sciences, as well as in materials science. The application of an array of fluorophores has made it possible to identify cells and sub-microscopic cellular components with a high degree of specificity (Fig. 3). These molecules can be conjugated to ...
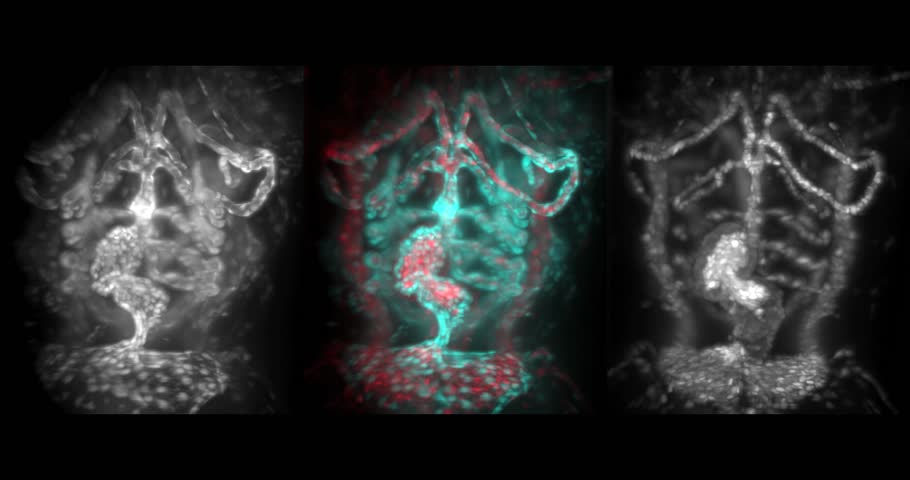
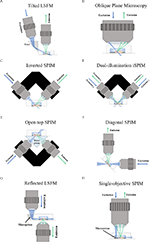
PDF Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy - UConn Health With light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) - also known as selective plane illumination microscopy (SPIM) - a conceptually new method was introduced to fluorescence live imaging in 2004. This development by Ernst Stelzer and his group at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, published in Huisken et al 2004, 5

Experimental configurations of single-molecule fluorescence microscopy.... | Download Scientific ...
Fluorescence microscope - Wikipedia The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design shown in the diagram.Light of the excitation wavelength illuminates the specimen through the objective lens. The fluorescence emitted by the specimen is focused to the detector by the same objective that is used for the excitation which for greater resolution will need ...
Fluorescent Dyes in Microscopy - Types, Vs Proteins, Applications Etc. Overview. Fluorescent dyes (also known as fluorophores/reactive dyes) may simply be described as molecules (non-protein in nature) that, in microscopy, achieve their function by absorbing light at a given wavelength and re-emitting it at a longer wavelength. This produces fluorescence of different colors that can be visualized and analyzed.
PDF In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images The z-stacks of transmitted-light microscopy images were acquired with different methods for enhancing contrast in unlabeled images. Several different fluorescent labels were used to generate fluorescence images and were varied between training examples; the checkerboard images indicate fluorescent labels that were not acquired for a given ...
Fluorescence Microscopy | Solutions | Leica Microsystems Fluorescence Light Microscopes Commonly, Fluorescence microscopes used in research applications are based on a set of optical filters: an excitation filter,; a dichroic beam splitter, and; an emission filter.; The excitation filter selects the wavelengths to excite a particular dye within the specimen, the emission filter serves as a kind of quality control by letting only the wavelengths of ...
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY/CELL BIOLOGY: The planar truth about light-sheet microscopy | Laser ...
› pmc › articlesSuper resolution fluorescence microscopy - PMC Among the various microscopy techniques, fluorescence microscopy is one of the most widely used because of its two principal advantages: Specific cellular components may be observed through molecule-specific labeling, and light microscopy allows the observation of structures inside a live sample in real time.
Fluorescent Labels - Neon Labels Inkjet/Laser | OnlineLabels.com® Our fluorescent label materials are bright, highly visible, neon colored labels with a permanent adhesive. The various five colors are ideal for signage, product labeling, organization, color coding and more. They have a matte finish that's great for printing logos, text, and designs and are both laser and inkjet printable for flexibility in ...
Fluorescent tag - Wikipedia Fluorescent tag. S. cerevisiae septins revealed with fluorescent microscopy utilizing fluorescent labeling. In molecular biology and biotechnology, a fluorescent tag, also known as a fluorescent label or fluorescent probe, is a molecule that is attached chemically to aid in the detection of a biomolecule such as a protein, antibody, or amino acid.
Fluorescent and photo-oxidizing TimeSTAMP tags track protein fates in ... Using new fluorescent photo-oxidizing tags, we show by correlated light and electron microscopy that newly synthesized PSD95 molecules rapidly incorporate beneath the postsynaptic membrane at ...

Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy ...
Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells Researchers have developed a new fluorescent label that gives a clearer picture of how DNA architecture is disrupted in cancer cells. ... Pathologists routinely use traditional light microscopes ...
In silico labeling: Predicting fluorescent labels in unlabeled images 4: Figure S4 Dependence of network performance on z-stack size with comparison to other models, related to Figures Figures1 1 and and3 3 and Methods S1 (A) Dependence of network performance on the number of images in the transmitted light z-stack.The x-axis is the number of images in the network input.The y-axis is the cross entropy loss on fluorescence label prediction on a validation set.

Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy ...
UCD Advanced Light Microscopy Core Facility Home Page Advanced Light Microscopy Core (ALMC) ... The ALMC can assist you with fluorescent and label-free imaging of various cellular structures or tissues in several ways including, but not limited to: Confocal Imaging - for obtaining crisp images with good z-resolution and for 3D imaging (diffraction limited resolution: 200nm in-plane and 500nm ...



Post a Comment for "45 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"